Do you get a fast Wi-Fi signal when sitting near your 5GHz router but instantly lose connection when moving to another room?
Do not blame your internet speed because the problem may be in your router signal all this time but Wi-Fi bandwidth.
Although faster and more robust than previous connections, 5 GHz Wi-Fi will fail to penetrate through walls.
Although Wi-Fi signals are known to pass through surfaces, 5GHz may not do the job, requiring significant upgrades.
Read on to find out how wall material, thickness, Wi-Fi band, and radio connection may affect the level of your Wi-Fi signal.
Table of Contents Show
Does Wi-Fi Signal Go Through Walls?
Wi-Fi or Wireless Fidelity is a long radio wave that quickly passes through any surface, including walls and doors.
Therefore, users install a router in one room and effectively connect to it from different parts of the home.
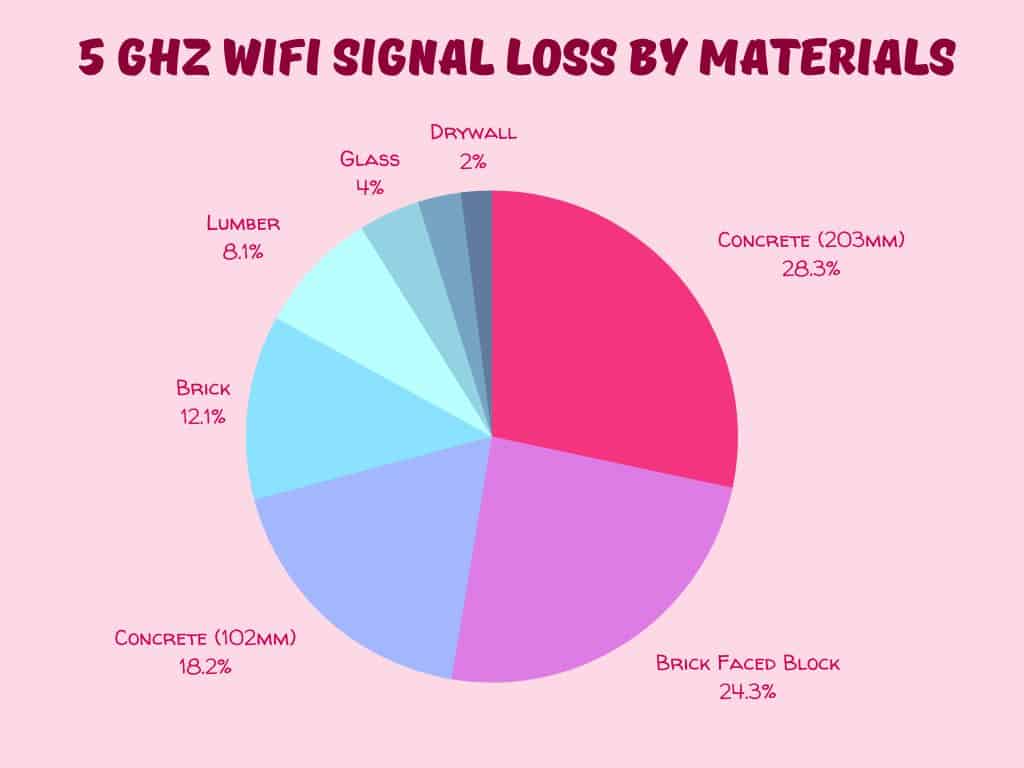
That being said, the level of signal attenuation will depend on the surface material it passes through.
Some surfaces are thicker and more compact, affecting Wi-Fi’s signal attenuation (penetration), such as internet speed, penetration, and connectivity.

Therefore, you can connect and effectively use Wi-Fi when separated by a glass wall compared to a concrete or steel wall.
For instance, a concrete wall with reinforced concrete contains 8″ thick slabs, usually applied in commercial or residential buildings.
Hence, the internet connection could be weaker through concrete than the drywall that is hardly 2″ thick.
Similarly, the Wi-Fi signal could be more robust in the upper stories separated by standard ceilings than in an adjoining room separated by a thick load-bearing wall.
Therefore, the signal has to penetrate the load-bearing wall, leading to weaker signal attenuation.
Here is the list of surface materials and their signal attenuation to give your a better idea.
| Material | 2.4 GHz | 5 GHz |
|---|---|---|
| Wooden door | 4 dB | 7 dB |
| Concrete wall | 20 dB | 30 dB |
| Plain glass window | 3 dB | 8 dB |
| Steel door | 20 dB | 30 dB |
| Human body | 3 dB | 5 dB |
| Trees/Vegetation | 0.5 dB/mtr | 1 dB/mtr |
Does 5GHz Wi-Fi Penetrate Through The Wall?
Although 5 GHz guarantees faster internet speed, it may fail to penetrate the thick walls of your home or office.
GHz stands for gigahertz, where the higher the GHz number, the faster the speed.
5 GHz, also known as 5G, has become popular for many internet users who demand higher and faster internet speed, especially for gaming, streaming, and work.
However, it lacks the latency that helps the signal travel farther distances, primarily through hurdles like walls and ceilings.
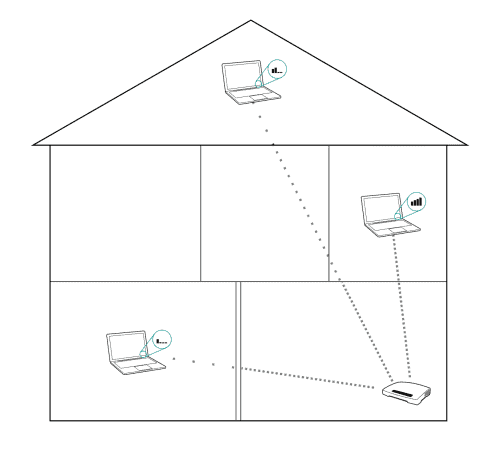
With a much shorter range, it may be easily blocked by concrete and dry walls.
Therefore, if installing a new router with 5 GHZ speed, you should be wary about where you will be seated when using the internet.
How Far Can 5 GHz Wi-Fi Travel?
The lower the GHz, the farther it will travel. For example, 2 GHz or 2G can travel 150 feet indoors and 300 feet outdoors.
Similarly, 3G and 4G can travel about 100 feet indoors when obstructed.
However, the 5GHz or 5G wavelength is the shortest and can only travel about 50 feet (15 meters) when unobstructed.
Due to this, the 5G signals can easily be blocked by physical barriers at home, like walls and electronic devices.
What May Restrict The 5 GHz Signal? (With Solutions)
5 GHz signal boasts a short wavelength compared to older generations of signal; therefore, it is often interrupted by different factors.
Here are a few factors that may restrict the 5 GHz signal.
1. Size Of Your Home
The larger the home, the weaker the Wi-Fi signal. As previously mentioned, 5 GHz boasts a shorter wavelength, limiting the signal to a specific distance.
The obstacles that may come in between in the form of walls, ceilings, and furnishings may limit its range.
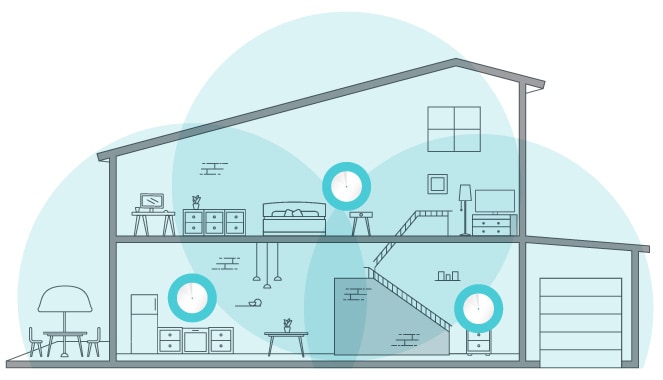
One effective way to solve this issue is to add an extender replicating the 5 GHz signal to other home parts.
It is recommended to plug the extender halfway between the router and the area you wish to reach.
Placing the extender farther from the router may risk losing significant signal speed.
2. Obstacles Or Materials
Obstacles such as metal blinds, doors, walls, reinforced surfaces, and furniture will significantly restrict the 5 GHz Wi-Fi signal.
Remember, metal is good at absorbing electromagnetic signals such as Wi-Fi, limiting the signal attenuation.
Similarly, the signal will be affected by reinforced concrete walls, plaster, and metal lath used in plaster, ceramic tiles, tinted glass, and low-emissivity surfaces.
Some other materials such as mirrors, drywall, and neighbor’s Wi-Fi network will also affect 5 GHz signal attenuation.
Try placing the router and using it in home parts with fewer obstacles; otherwise, invest in an excellent extender to replicate the Wi-Fi signal.
3. Signal Interferences
The 5 GHz band may work very well at a short distance but often encounters interferences with other signals.
Some standard household devices like Bluetooth, baby monitors, garage door openers, Walkie, and Microwave may interfere with the 5 GHz signal.
5 GHz operates at a more significant number of unique channels, which would work well when less overlapped with other signals.
Therefore, keeping the device and router closer will solve this problem.
Otherwise, installing the router at a higher elevation near the ceiling, sideboard, or shelf may also help combat this problem.
4. Interference With 2.4 GHz Router
Mixing the 5 GHz bands with the 2.4 GHz bands can be a grave mistake.
The 5 GHz router does not readily mix with the 2.4 GHz router, creating interferences that may disqualify both 5 GHz networks.
As a solution, you should upgrade to a single router with a dual-band, so neither signal interferes.
On the other hand, the 2.4 GHz band upgraded to 802.11g speed will run faster than the 5 GHz bands, eliminating the need to get the latter band altogether.
5. Location Of The Router
If you have two different routers at home, consider placing them far from each other to eliminate interference.
You may also find the Wi-Fi signal is better in a different part of the House, such as a room without reinforced and load-bearing walls.
Similarly, they are better kept in the adjoining room or a straight line as the line of sight is essential for radio wave travel.
Alternatively, consider adding the Wi-Fi repeater to another part of the home using a cable to improve the signal.
5GHz Vs. 2.4GHz Wi-Fi Signals
2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Wi-Fi signals vary regarding wavelength range, speed, and usage.

Here are brief differences between the two frequencies.
| 2.4 GHz | 5 GHz |
|---|---|
| It boasts longer wave length range with better signal attenuation, meaning it can penetrate obstacles. | It boasts shorter wave length range, which may interfere with obstacles. |
| It travel with lower speed; hence devices at a farther distance may experience slower connection. | 5 GHz boasts higher data rate and travel faster, so devices kept within 50 feet will experience better speed. |
| It may interfere with other electronic devices that use 2.4 GHz frequency such as microwave, monitors, remote cameras, etc. | Electronic devices will only interfere with the signal when kept close to each other. |
| The internet may be slower for intensive activities, requiring upgrading to higher bandwidth networks. | 5 GHZ is better for intensive internet activities such as gaming, streaming, and video conferencing. |
| 2.4 GHz travels farther at lower speeds. | 5 GHz provides faster speeds at shorter range. |
| Upgarding 2.4 GHz with 802.11b to 802.11g can help achieve faster and higher bandwith, up to 54 Mbit/s | Obtaining 5 GHz upgarded to 802.11ac can help combat issues with interferences. |
Tips To Improve 5 GHz Wi-Fi
Here are a few tips to improve the 5 GHz Wi-Fi connection.
- Place your router in an elevated region and as close to the device as possible.
- Avoid placing it inside a room with steel beams and reinforced concrete walls.
- Upgrade your 5 GHz router with antennas to boost internet speed, even up to 1 Gbps.
- Choose the right Wi-Fi channel, as 5 GHz has up to 24 channels. For the laptop channel, close to 5.83, and for the phone channel, 5 will be better.
- Keep your router updated by upgrading firmware or router updates.
- Prevent bandwidth hoggers from stealing bandwidth from other devices.
- Use performance-enhancing features like Multi-user MIMO, beam forming, etc., to boost internet speed.
- Protect your Wi-Fi router with a password, so hackers may not get easy access.
- Buy a Wi-Fi repeater or extender as needed to extend the signal throughout the area.
- Regularly reboot your router to refresh the connection and the router’s memory cache.

The Bottom Line
The 5 GHz Wi-Fi signals are best for modern-day activities and devices but may fail to penetrate through walls.
Therefore, boosting the Wi-Fi connection using different methods may help eliminate frequent interferences.
Otherwise, upgrading the router with a better connection and placing the device closer to the router will help solve the problem.
Follow this guide to find effective ways to improve your 5 GHz Wi-Fi connection.


